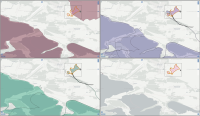
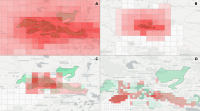
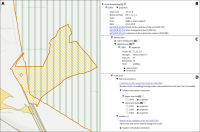
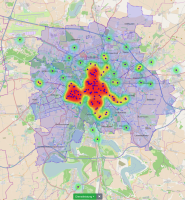
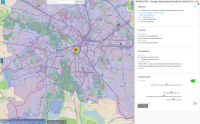
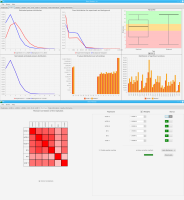
Experts face the task to decide where and how land reuse---transforming previously used areas into landscape and utility areas---can be performed. This decision is based on which area should be used, which restrictions exist, and which conditions have to be fulfilled for reusing this area. Information about the restrictions and the conditions is available as mostly textual, non-spatial data associated to areas overlapping the target areas. Due to the large amount of possible combinations of restrictions and conditions overlapping (partially) the target area, this decision process becomes quite tedious and cumbersome. Moreover, it proved to be useful to identify similar regions that have reached different stages of development within the data set which in turn allows determining common tasks for these regions. We support the experts in accomplishing these tasks by providing aggregated representations as well as multi-coordinated views together with category filters and selection mechanisms implemented in an interactive decision support system. Textual information is linked to these visualizations enabling the experts to justify their decisions. Evaluating our approach using a standard SUS questionnaire suggests, that especially the experts were very satisfied with the interactive decision support system.
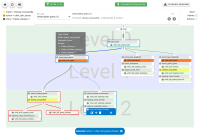
A chatbot can automatically process a user's request, e.g. to provide a requested information. In doing so, the user starts a conversation with the chatbot and can specify the request by further inquiry. Due to the developments in the field of NLP in recent years, algorithmic text comprehension has been significantly improved. As a result, chatbots are increasingly used by companies and other institutions for various tasks such as order processes or service requests. Knowledge bases are often used to answer users queries, but these are usually curated manually in various text files, prone to errors. Visual methods can help the expert to identify common problems in the knowledge base and can provide an overview of the chatbot system. In this paper, we present Chatbot Explorer, a system to visually assist the expert to understand, explore, and manage a knowledge base of different chatbot systems. For this purpose, we provide a tree-based visualization of the knowledge base as an overview. For a detailed analysis, the expert can use appropriate visualizations to drill down the analysis to the level of individual elements of a specific story to identify problems within the knowledge base. We support the expert with automatic detection of possible problems, which can be visually highlighted. Additionally, the expert can also change the order of the queries to optimize the conversation lengths and it is possible to add new content. To develop our solution, we have conducted an iterative design process with domain experts and performed two user evaluations. The evaluations and the feedback from our domain experts have shown that our solution can significantly improve the maintainability of chatbot knowledge bases.
Accepted as Fullpaper at WSCG 2022.
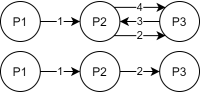
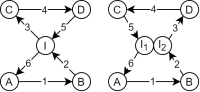
Land Reuse processes are large planning and decision-making processes based on a large amount of geographic data. Therefore, it is essential that this data is as accurate as possible. However, errors can occur during the creation of the data and not all of them are directly noticeable. We report here what errors we have encountered while working with this geographic data, what problems they can cause, and how we have fixed them. Since the correction can be very time-consuming with the enormous amount of data, we have focused on an automatic correction. Not all of this data can be corrected this way, for the rest, we briefly indicate a procedure to support and simplify the manual correction.
Municipal authorities have, among other tasks, a great interest in supporting their local economy. For this purpose, they provide consulting offices that advise companies and mediate cooperation partners.
The city administration of Leipzig created a business register in which companies can provide their competences in free text fields. This business register contains over 1000 entries and it is not straight forward to find and compare companies based on their self-descriptions.
In this paper, we propose a new visualization to analyze the distribution of local companies and exploring the competence profiles of the companies. In order to visualize connections between companies, we perform a semantical analysis. In detail, we use the management staff listing and the core competence descriptions to link the entries. The company location and the connections between the companies are visualized on a map or as a graph. The visualization provides several filtering and interaction mechanisms on demand. From a governance perspective, this leads to insights into company and industry sector networks within a local economic zone.
Sierra Platinum is a fast and robust peak-caller for replicated ChIP-seq experiments with visual quality-control and -steering. The required computing resources are optimized but still may exceed the resources available to researchers at biological research institutes. Sierra Platinum Service provides the full functionality of Sierra Platinum: using a web interface, a new instance of the service can be generated. Then experimental data is uploaded and the computation of the peaks is started. Upon completion, the results can be inspected interactively and then downloaded for further analysis, at which point the service terminates.